1) Please go through the patient data in the links below and answer the following questions:
26 year old woman with complaints of altered sensorium somce 1 day,headache since 8 days,fever and vomitings since 4 days
Case presentation links:
a). What is the problem representation of this patient and what is the anatomical localization for her current problem based on the clinical findings?
- 26 year old female married 10yrs back mother of 2 children tailor & agricultural labourer by occupation presented to casualty in a state of altered sensorium & irrelevant talk
- C/o headache since 1 month which increased in last 10 - 15 days associated with vomitings since 1 week and fever, neck pain , generalized weakness since 4 days and altered sensorium with irrelevant talk since 1 day.
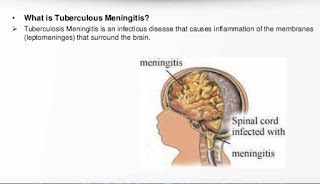
- Diagnosed as TB meningitis
b) What is the etiology of the current problem and how would you as a member of the treating team arrive at a diagnosis? Please chart out the sequence of events timeline between the manifestations of each of her problems and current outcomes.
1.Mycobacterium TB according to CBNAAT done for CSF is positive.
2. Hyponatremia
3.TB meningitis
6 years back Both hands small joints pain progressed to elbow and shoulder - relieved with treatment at local RMP
3years back multiple joint pains - diagnosed as SLE & started on
treatment.
In 2020 (december): - headache on& off several times/week relieved with treatment
Increased headache from 15 days.10 days back stopped methyl prednisolone vomitings from 1 week
Fever, neckpain, generalized weakness & decreased appetite from 4 days admitted to local hospital at night
went to bathroom and fell down in a state of altered sensorium.Same day presented to our casualty @ around
3 am in a state of altered sensorium & irrelevant speech
c) What is the efficacy of each of the drugs listed in her prior treatment plan that she was following since last two years before she stopped it two weeks back?
Hydrochloroquine200mg/OD,
Sulfasalazine,
Methylprednisolone,
Alandronic acid and Cholecalciferol,
Aceclofenac,
Flupirtine,
Gabapentine,
Methylcobalamin tablets which she stopped 10 days back.
-Hydroxychloroquine (HCQ) is an alkalinizing lysosomatropic drug that accumulates in lysosomes where it inhibits some important functions by increasing the pH. HCQ has proved to be effective in a number of autoimmune diseases including systemic lupus erythematosus (SLE)
For example:
Why was she given bisphosphonates?
What is the efficacy of using primary bisphosphonate prophylaxis for patients started on corticosteroids?
-
Bisphosphonates reduce the risk of vertebral fractures and the prevention and treatment of steroid‐induced bone loss
.
What is the efficacy of using primary PPI prophylaxis during initiation of any corticosteroids to prevent Gi ulcers?
Use of corticosteroids causes peptic ulcer ,however it is not recommended routinely because it is a rare complication observed in 0.4-1.8% patients .
d) Please share any reports around similar patients with SLE and TB meningitis?
Any reports of normal csf leukocyte count and normal csf protein in meningitis?
What could be the probable cause for a normal csf leukocyte count in a patient with chronic meningitis?
Meningitis in the absence of pleocytosis on CSF is rare. If this occurs, causative organism is likely bacterial.
e) What is the sensitivity and specificity of ANA in the diagnosis of SLE?
The estimated sensitivity and specificity of the ANA test for SLE were 100% and 86%, respectively. The positive predictive value of the ANA test was 11% for SLE and 11% for other rheumatic diseases.
2) Please go through the two thesis presentations below and answer the questions below by also discussing them with the presenters:
What was the research question in the above thesis presentation?
Association of serum magnesium with type-2 diabetes mellitus
What was the researcher's hypothesis?
Hypomagnesemia in diabetes was associated with poorer glycemic control, retinopathy, nephropathy, and foot ulcers.
What is the current available evidence for magnesium deficiency leading to poorer outcomes in patients with diabetes?
What was the research question in the above thesis presentation?
24 hrs urinary sodium excretion values in newly diagnosed hypertensive patients.
What was the researcher's hypothesis?
Low level of urinary sodium excretion related to low rate of hypertension and slower BP increase with age and better prognosis.
What is the current available evidence for the utility of monitoring salt excretion in the hypertensive population?
https://www.researchgate.net/publication/40679439_Usefulness_of_Self-Monitoring_of_Urinary_Salt_Excretion_in_Hypertensive_Patients
3) Please critically appraise the full text article linked below:
What is the efficacy of aspirin in stroke in your assessment of the evidence provided in the article. Please go through the RCT CASP checklist here
https://casp-uk.net/casp-tools-checklists/ and answer the questions mentioned in the checklist in relation to your article.
Aspirin treatment did not significantly reduce the frequency of stroke progression. Amongst aspirin‐treated patients, stroke progression occurred in 15.9% as compared with 16.7% in the placebo group, which is less frequent than expected. The relative risk was 0.95 (95% CI 0.62–1.45) in the treatment group. As regards patient outcome at discharge and after 3 months, aspirin treatment did not show any difference.
| Aspirin (n = 220) | Placebo (n = 221) |
|---|
| Mean age (years) | 74.1 (72.7–75.4) | 74.2 (72.9–75.5) |
| Gender (men, %) | 52.7 | 49.8 |
| Hypertension (%) | 34.6 | 37.3 |
| Diabetes mellitus (%) | 14.6 | 16.8 |
| Stroke (%) | 7.3 | 4.6 |
| Atrial fibrillation (%) | 14.1 | 16.2 |
| Condition at admission |
| SSSS (7–27), mean points | 13.2 (12.6–13.7) | 12.3 (11.8–12.7) |
| SBP (mean, mmHg) | 165 (161–168) | 166 (162–170) |
| DBP (mean, mmHg) | 90 (88–92) | 89 (87–91) |
| Blood glucose (mmol L−1) | 5.9 (5.6–6.3) | 6.4 (6.0–6.8) |
| Haemoglobin (g L−1) | 142 (140–144) | 141 (139–143) |
| Leucocytes (×109 L−1) | 8.6 (8.0–9.1) | 8.3 (8.0–8.6) |
| Platelets (×109 L−1) | 229 (221–237) | 235 (225–245) |
| Delay onset – admission (h) | 10.0 (8.8–11.2) | 9.3 (8.2–10.3) |
| PACIa (%) | 76.0 | 75.1 |
| TACI (%) | 2.3 | 1.8 |
| LACI (%) | 18.4 | 19.9 |
| POCI (%) | 3.2 | 3.2 |
| Final diagnosis (%) |
| Cerebral thrombosis | 80.9 | 76.0 |
| Cerebral embolism | 16.2 | 21.3 |
| TIA | 2.3 | 2.7 |
- SSSS, Scandinavian Stroke Supervision Scale; SBP, systolic blood pressure; DBP, diastolic blood pressure; PACI, partial anterior circulation infarcts; TACI, total anterior circulation infarcts; LACI, lacunar infarcts; POCI, posterior circulation infarcts; TIA, transient ischaemic attack.
4) Please mention your individual learning experiences from this month.
-Water hammer pulse-AR
-Clubbing causes -bilateral ,unilateral and unidigital clubbing
-Dulzihims sign-AR
-Trops murmur
-Carotid and jvp
-Liver abscess(donot aspirate or puncture without liquefaction
-Alcohol dependance syndrome
-Edema -pitting based on dips >1min-heart failure <1min-hypoAlbuminea
-Finger tingling -cervical spondylitis alcoholic dm ,neck rotating test -cervical spondylitis (tiredness ,faint)
-Abdominal reflex
-MI~ <12hrs -thrombolysis-then PCA
>12hrs-PCA
Thrombolysis -streptokinase(cheap and easily available )
-Central line guided by DR.AJITH
-chronic pancreatitis
-use of pancreatitis enzymes for treatment of pain in chronic pancreatitis
5) a) What are the possible reasons for the 36 year old man's hypertension and CAD described in the link below since three years?
Patient was a chronic smoker and alcoholic which could be the risk factors for his HTN AND CAD.
b) Please describe the ECG changes and correlate them with the patient's current diagnosis.
Rythm - Initial ecgs rate is Irregular with VPC ,later becoming regular
Axis - Normal
VPCs followed by a compensatory pause
QS complexes in v1 - v3Poor R wave progression
T-wave inversions in v4 - v6
Mild ST segment elevation in v1 - v4
c) Share an RCT that provides evidence for the efficacy of primary PTCA in acute myocardial infarction over medical management. Describe the efficacy in a PICO format.
P-214 patients with stable angina, normal ventricular function and a proximal stenosis of the left anterior descending coronary artery > 80%
I-Balloon angioplasty
Medical therapy alone
C-Balloon angioplasty (n = 72)
Medical therapy alone (n = 72)
O-At an average follow-up period of 3 years
p = 0.28, angioplasty vs. medical treatment
There was no difference in mortality or infarction rates among the groups


Comments
Post a Comment